Eradicating a gene that manages stress inside insulin-producing beta cells attracts useful consideration from the immune system, defending mice predisposed to kind 1 diabetes from growing the illness, a brand new College of Wisconsin–Madison research reveals.
The research additionally discovered that modifications found within the modified mouse beta cells are additionally current in human beta cells that handle to outlive the widespread beta-cell demise that characterizes kind 1 diabetes.
This provides the researchers hope that their findings, revealed within the journal Cell Metabolism, could level to a possible new remedy that may very well be administered very early within the growth of diabetes. Kind 1 diabetes afflicts as many as 20 million individuals all over the world, contributing to glaucoma, nerve injury, hypertension and stroke. In america, it shortens life expectancy by greater than a decade.
“Once we eat, our beta cells produce about 1 million molecules of insulin each minute to assist preserve regular blood glucose ranges,” says Feyza Engin, a UW–Madison professor of biomolecular chemistry and senior writer of the brand new research. “That could be a huge and traumatic job, particularly for part of these beta cells known as the endoplasmic reticulum.”
The endoplasmic reticulum is just like the cell’s warehouse employees. It folds the insulin protein molecules {that a} beta cell produces, packing them for transport to different elements of the physique. If one thing goes mistaken with the protein folding course of, the transport course of backs up and even stops, stressing the endoplasmic reticulum. A stress-response gene known as Atf6 perks up when a cell is battling unfolded proteins. But when Atf6 cannot resolve the protein-folding downside, extended stress will ultimately kill the cell.
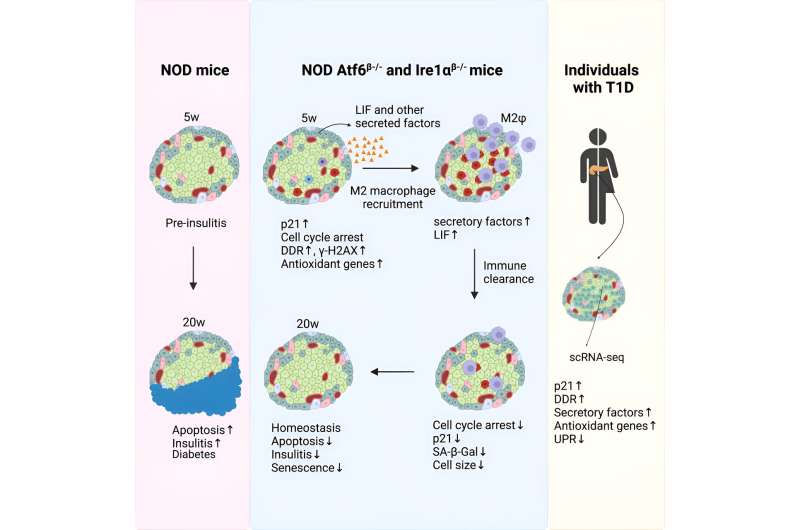
Engin’s lab bred a line of diabetes-predisposed mice with out the Atf6 gene of their beta cells. As an alternative of assembly their typical destiny, these mice had been protected against diabetes. Evaluation of the genes expressed by their beta cells prompt the cells entered a state known as senescence far forward of schedule.
Senescence is a interval of the cell’s life cycle during which it stops dividing and halts different regular mobile enterprise. Senescing cells may cause issues for neighboring cells by releasing inflammatory messaging molecules that set off an immune system response.
“We eliminated—knocked-out—the Atf6 gene within the beta cells within the pancreas of our mouse mannequin of kind 1 diabetes, and they didn’t turn into diabetic,” Engin says. “As an alternative of dying off, these cells unexpectedly seem to enter an early senescence state that initiated a helpful immune response and helped the cells survive an autoimmune assault.”
DNA injury, stress and growing old can kick off senescence, which may draw an immune system response that cleans up the senescent cells. If the immune system fails to clear these cells, they accumulate and trigger persistent irritation and illness.
“The beta cells with out Atf6 exhibit transient senescence and begin releasing this group of proteins, together with leukemia inhibitory issue, or LIF, that recruits protecting immune cells known as M2 macrophages,” Engin says.
Macrophages are white blood cells that eat issues—pathogens, overseas our bodies, useless cells—that do not belong within the physique. Within the pancreases of the Atf6-knockout mice, the M2 macrophages appeared to work across the altered beta cells, relieving irritation and serving to to cut back the buildup of different, detrimental senescent cells. This led to more healthy tissue and improved beta cell well being and performance, staving off kind 1 diabetes.
Much more thrilling, Engin says, is how carefully the brand new research’s ends in mice seem like mirrored in human cells.
With a blood check, medical doctors can establish people who find themselves at high-risk of growing kind 1 diabetes months upfront of the demise of their beta cells.
“Which may be an ideal timeframe for a remedy primarily based on pharmacological inhibition of Atf6 or induction of LIF and different secreted proteins,” says Engin. “If we are able to get there in time to guard these cells with transient senescence, the onset of diabetes could be prevented.”
Whereas almost all beta cells die off in diabetes, just a few—although too few to be efficient insulin suppliers—do survive. To see whether or not their mouse findings may very well be relevant in people, Engin’s lab, with collaborators at Case Western Reserve College, Université Libre de Bruxelle and the College of Manitoba, studied beta cell samples taken from diabetes sufferers.
“In these surviving beta cells, we discovered decreased Atf6 exercise and an early senescence gene expression sample, suggesting this similar course of that saved our mice from changing into diabetic could have labored to guard these residual beta cells in people,” Engin says.
The researchers hope to construct on these findings by delving additional into the function and potential advantages of senescence in kind 1 diabetes and different illnesses.




