A Rutgers professor and different researchers have carried out a scientific assessment and meta-analysis to guage research evaluating perinatal outcomes amongst people with gestational diabetes mellitus. Being pregnant weight and biochemical markers measured in blood from girls with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) have been associated to elevated danger of poor being pregnant outcomes, suggesting a brand new course for precision diagnostics, in line with researchers.
The research led by Ellen C. Francis, an assistant professor within the Division of Biostatistics and Epidemiology at Rutgers College of Public Well being, and revealed in Communications Drugs, evaluated the diagnostic worth of those markers earlier than or on the time of screening for GDM, a kind of diabetes that may develop throughout being pregnant.
“Though we discovered that weight problems is a danger issue for offspring born bigger for his or her gestational age, proof means that the metabolic alterations that accompany weight problems enhance the danger of opposed outcomes,” mentioned Francis. GDM, characterised by elevated blood sugar (glucose) ranges throughout being pregnant, is the commonest metabolic situation amongst pregnant girls and poses dangers to each mom and little one. Whereas normal therapies are utilized, medical outcomes can differ amongst people.
Francis mentioned the analysis demonstrates the necessity for a extra nuanced strategy to diagnose GDM, which can assist enhance outcomes. It’s the first systematic assessment of the literature to evaluate the potential of subtypes in GDM and to look at whether or not nonglycemic markers may refine danger stratification. Francis mentioned among the literature recommended insulin profiles and triglyceride ranges could function promising non-glucose indicators of danger.
“To actually assess the medical implications of precision diagnostics in GDM, we first want to grasp if insulin resistance or increased triglycerides are causally linked to opposed outcomes and whether or not we will safely goal them in being pregnant,” Francis mentioned.
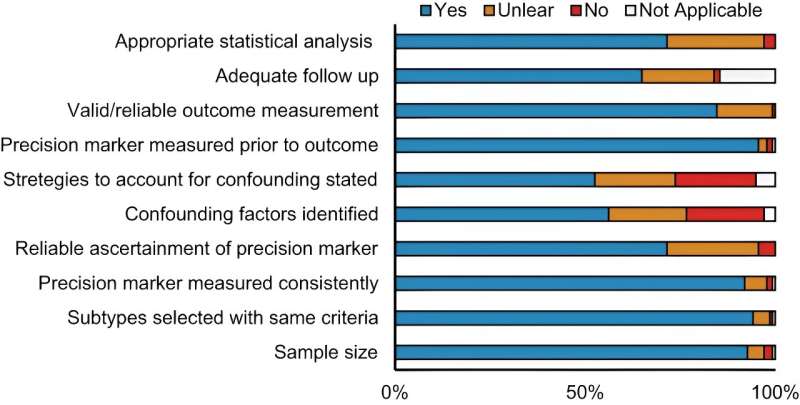
General, researchers discovered a essential hole within the present literature by which most research hadn’t targeted on evaluating medical, biochemical or sociocultural variations amongst girls who develop GDM.
“In our full-text screening of 775 research, we discovered that solely just lately has there been a concentrate on medical, biochemical, or sociocultural markers that would enhance who’s at best danger of poor outcomes and on evaluating medical outcomes between completely different subtypes of GDM,” mentioned Francis. “The information from these research point out that sooner or later, we might be able to refine how we diagnose GDM through the use of anthropometric or biochemical data together with present diagnostic approaches.”
Future analysis ought to delve into mechanistic research on precision biomarkers, massive various inhabitants research for replication, and multinational research specializing in environmental and behavioral components, Francis mentioned. It also needs to discover potential insights on informal pathways of heterogeneity inside GDM and its outcomes from genetic and multi-omics information utilizing superior analytical approaches.
Examine co-authors embrace researchers from collaborating establishments in the US, the UK, Singapore, South Korea, and Australia.




